FAILURE ANALYSIS GUIDELINES
Four Basic Failure Mechanisms: Design, Material, Processing and Environmental
Failure Analysis Protocol:
-
Gathering of Background Information and Selection of Samples
-
Review of Safety Considerations
-
Establishment of Record Keeping
-
Macroscopic (Visual) Examination and Analysis
-
Identification, Preservation and Cleaning of Samples
-
Microscopic Examination and Fractography
-
Determination of Failure Mechanism (“How it failed”)
-
Mechanical Testing
-
Stress Analysis (including Fracture Mechanics and FEA)
-
Chemical Analysis
-
Testing Under Simulated Service Conditions
-
Analysis of Evidence and Formulations of Conclusions (“Why it failed”)
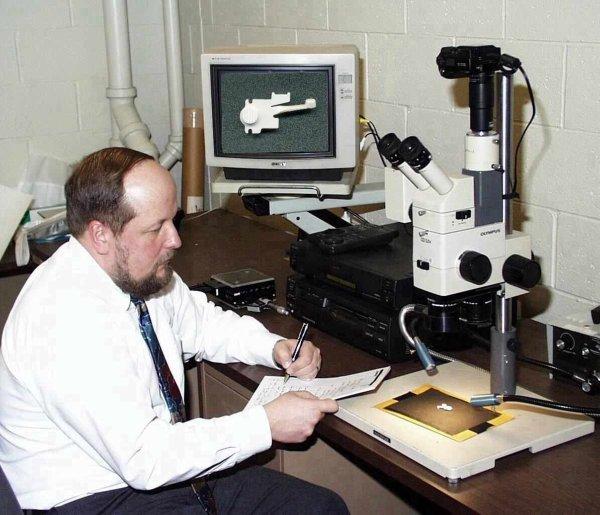

After data collection, visual inspection and photographic documentation, optical microscopy is often one of the most important steps to a failure analysis investigation.
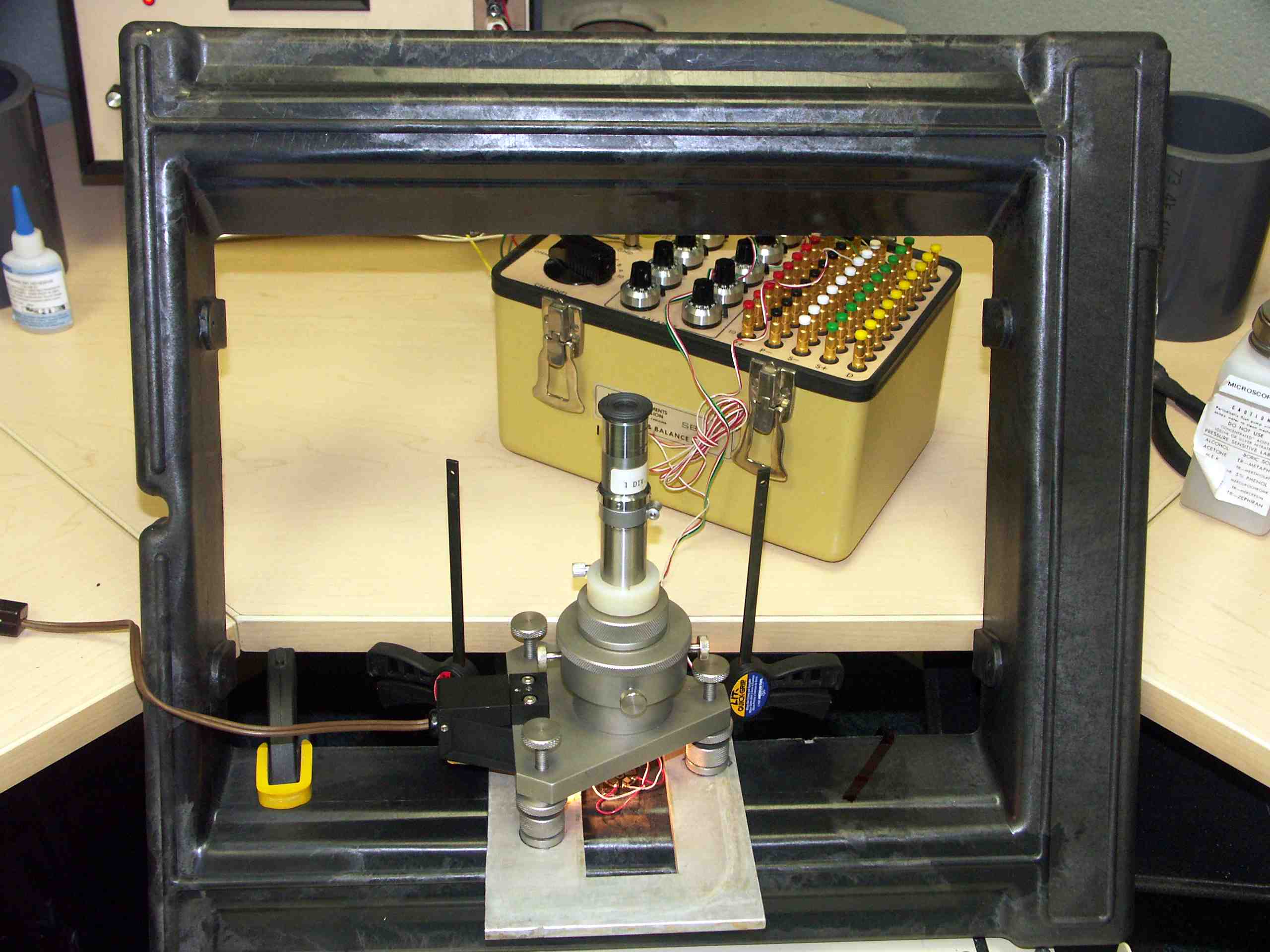

Residual stress measurement made on a glass-filled polymeric injection molded part.
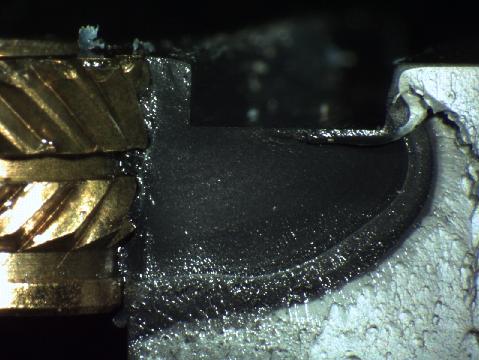
Slow crack growth fracture origin adjacent to a metal insert on a nylon housing was the result of environmental stress-cracking.
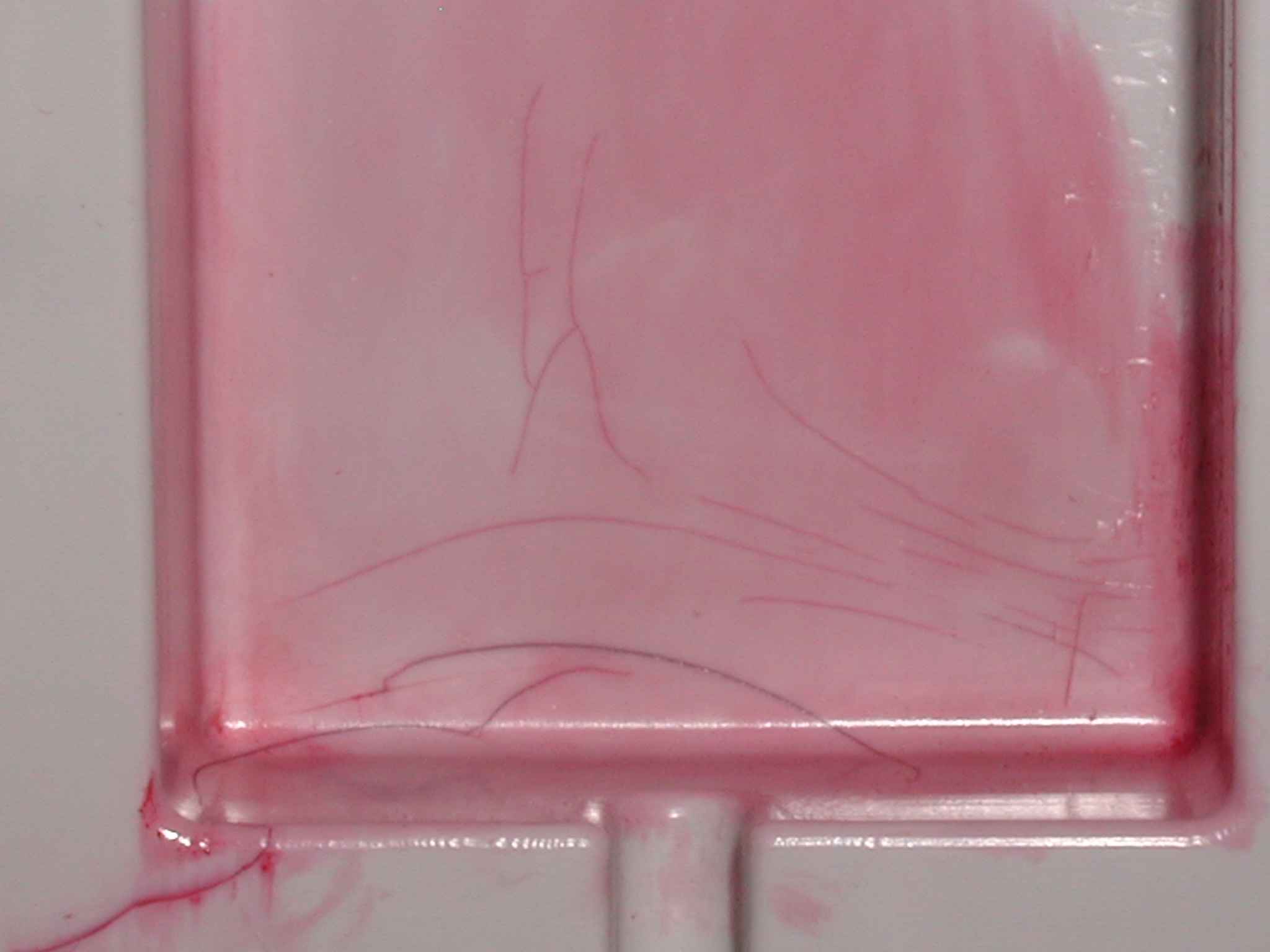

Environmental stress-cracking revealed on the inside of a medical device with the aid of a red-colored dye penetrant.
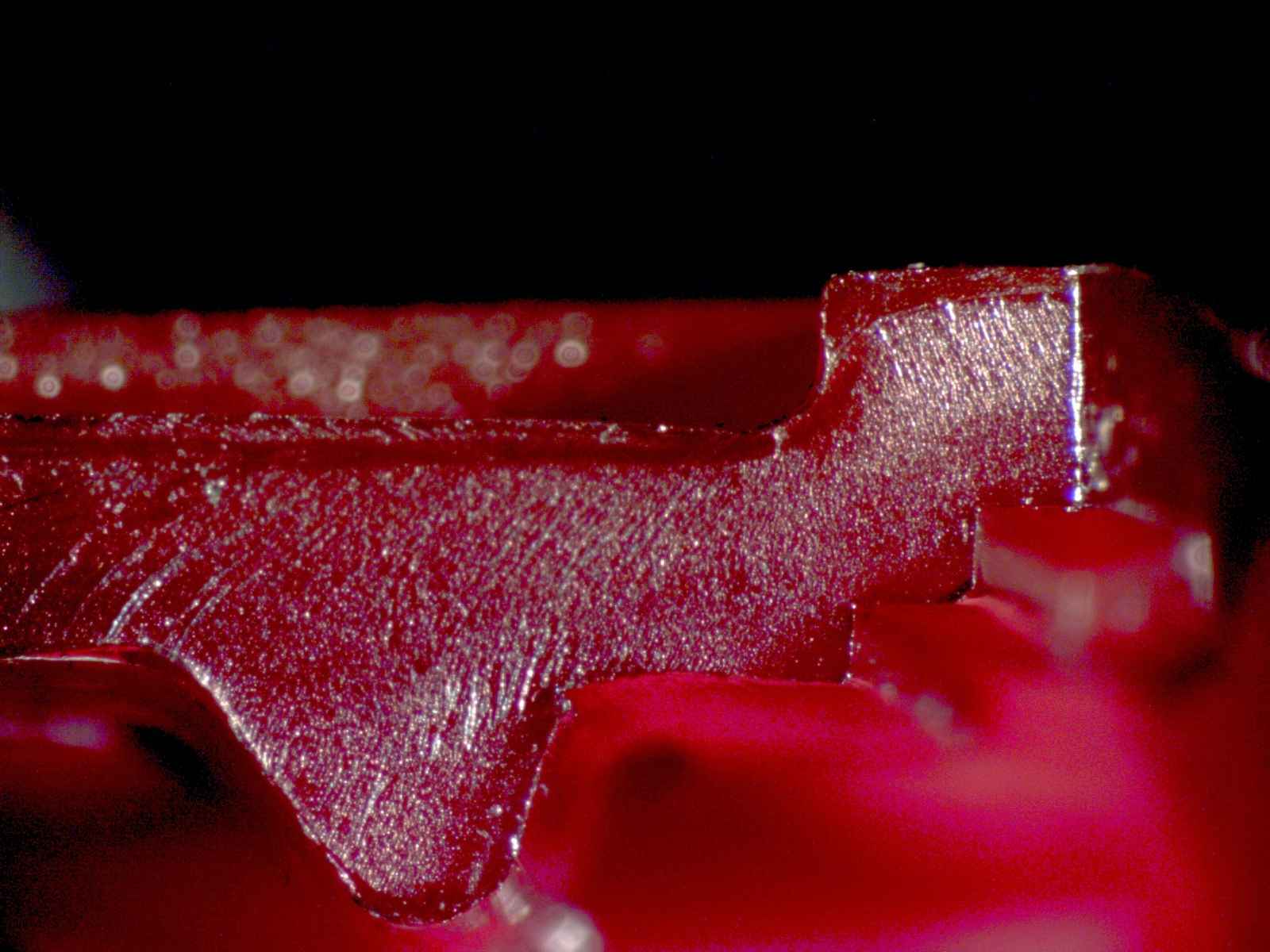

Bottle cap closure fractured cross-section with failure origins located in the inner "steps".
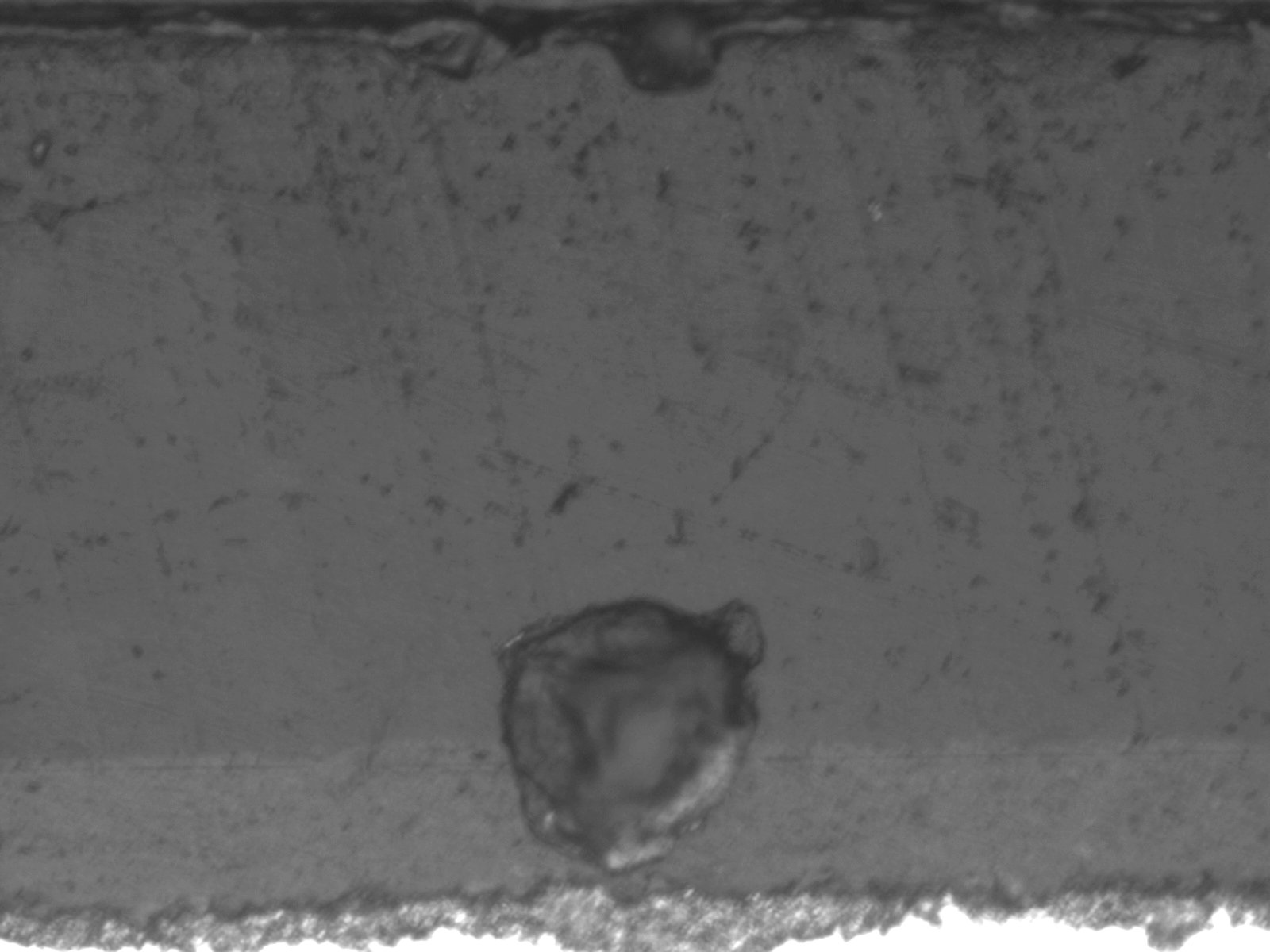
Cross-sectioned black powdercoated metal automotive trim panel reveals a large void formed at the subsurface epoxy layer extending into the powdercoat layer above. The surface "pinhole" defect is shown above.
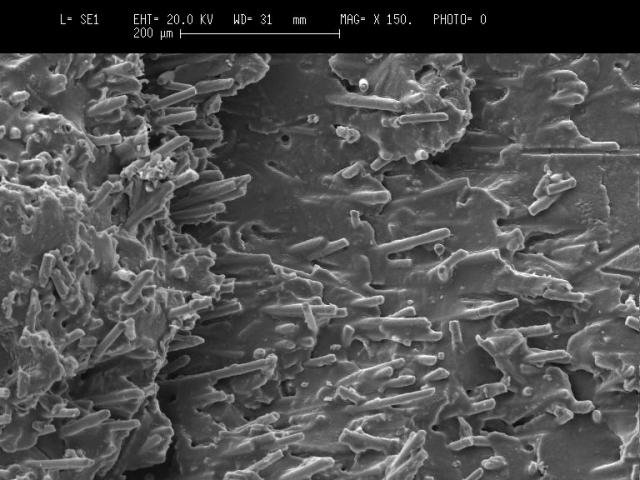

Fracture surface of a glass-fiber reinforced nylon filter housing with good adhesion of the fibers to the polymer matrix.

Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) with energy dispersive x-ray spectroscopy (EDS) is an extremely valuable tool for materials evaluation. SEM/EDS microscopy is particularly useful for fractographic examination, elemental mapping and phase determination, contaminant analysis, corrosion analysis, topographic analysis and particle size analysis.
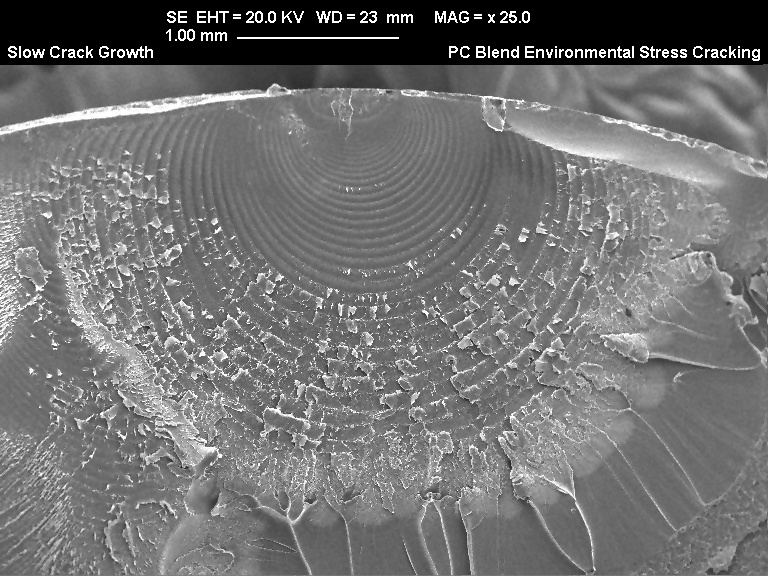
SEM micrograph of a slow crack growth fracture origin on a PC blend material due to enivronmental stress-cracking caused by the cutting solution in the presence of molded-in stress.

Fatigue sample fracture origin on a PC blend material.
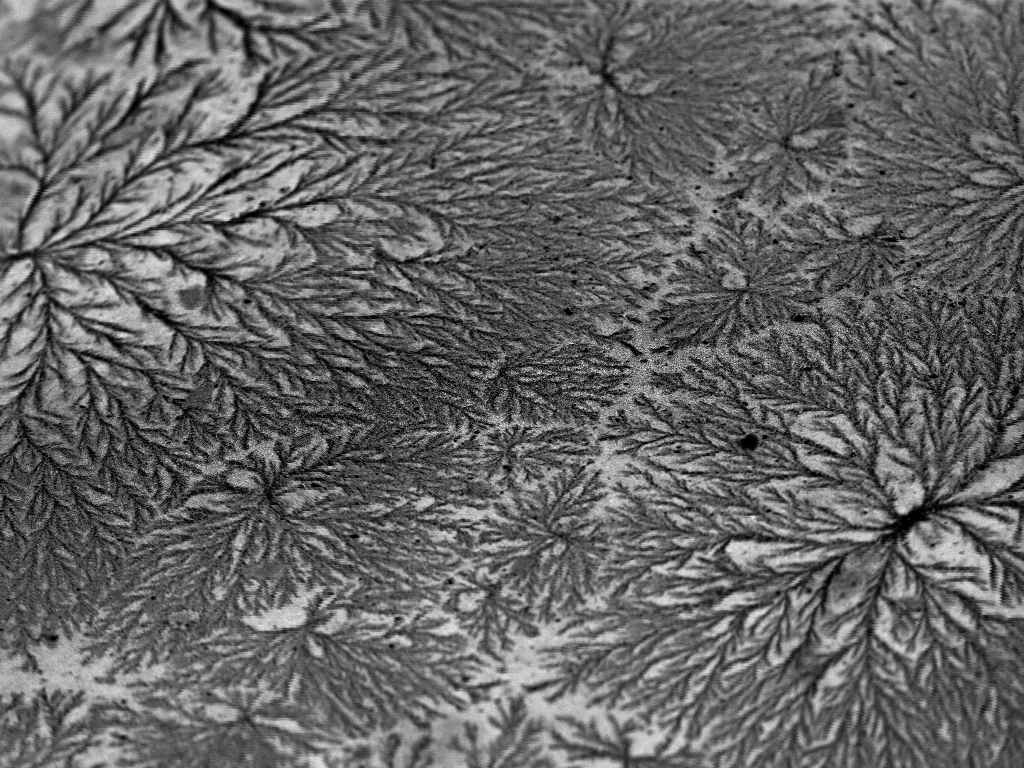
Dendritic crystalline formations due to residual sodium on a titanium catalyst surface, SEM micrograph.
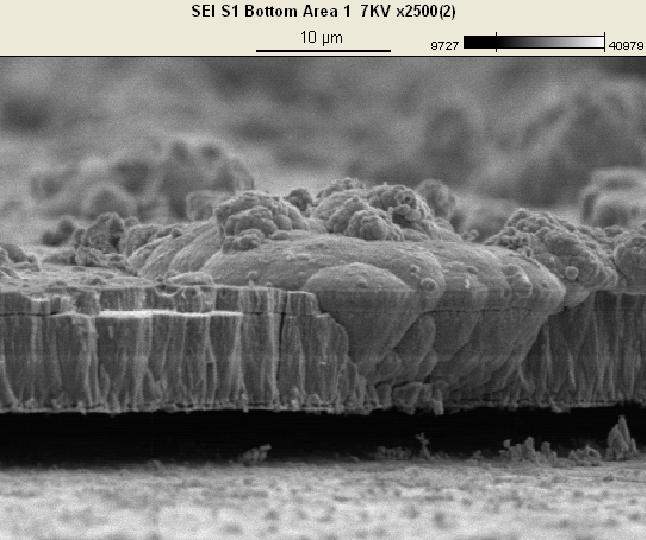
SEM micrograph of Iron-oxide scale deposited on a titanium catalyst.
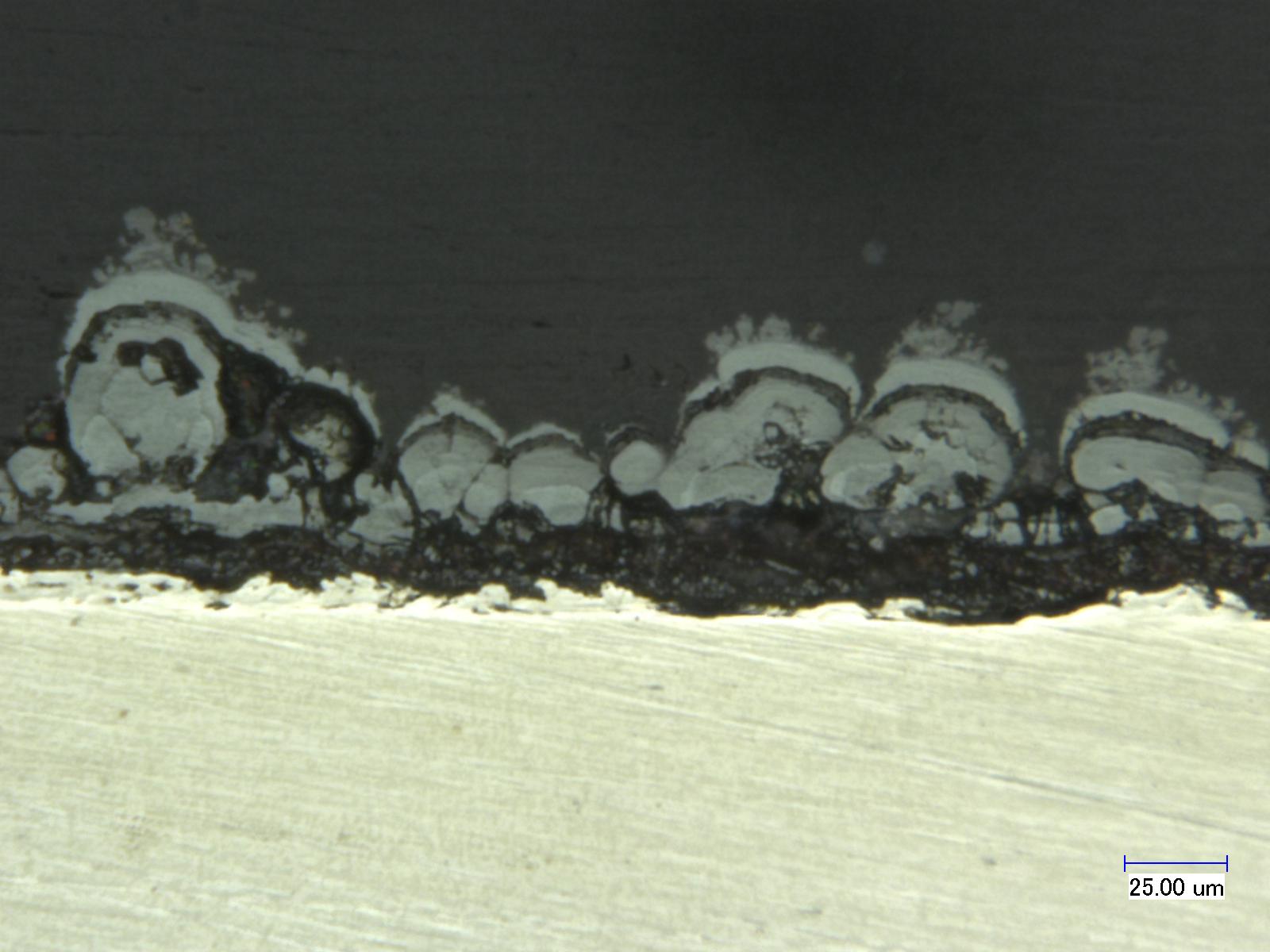
Cross-sectioned sample of Iron-oxide on a titanium substrate.
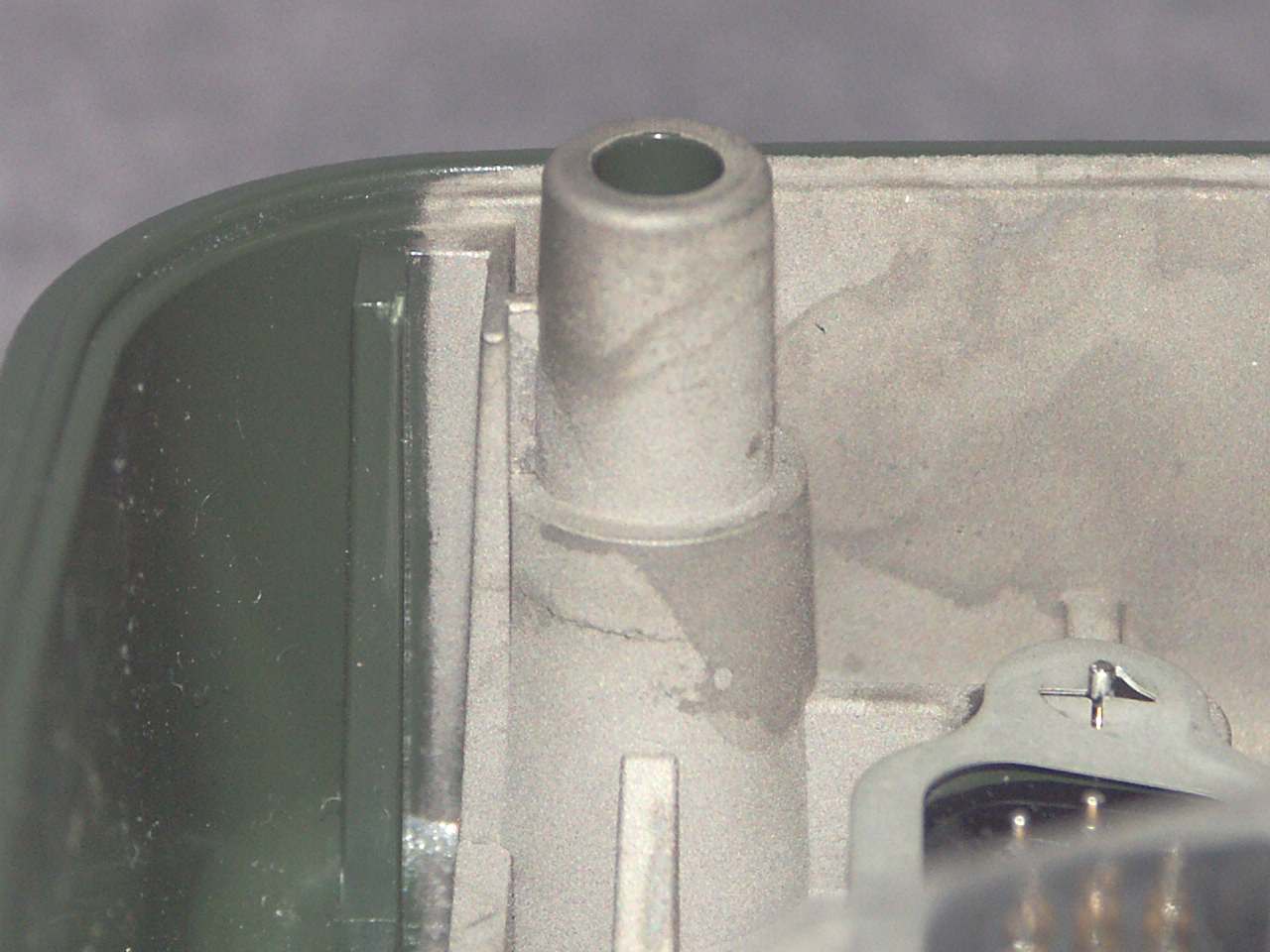
Side view of a crack on a screw boss stanchion that failed due to marginal material that was degraded during processing in conjunction with stress from assembly torque and thermal cycling during quality testing.